Our Approach
Analysis
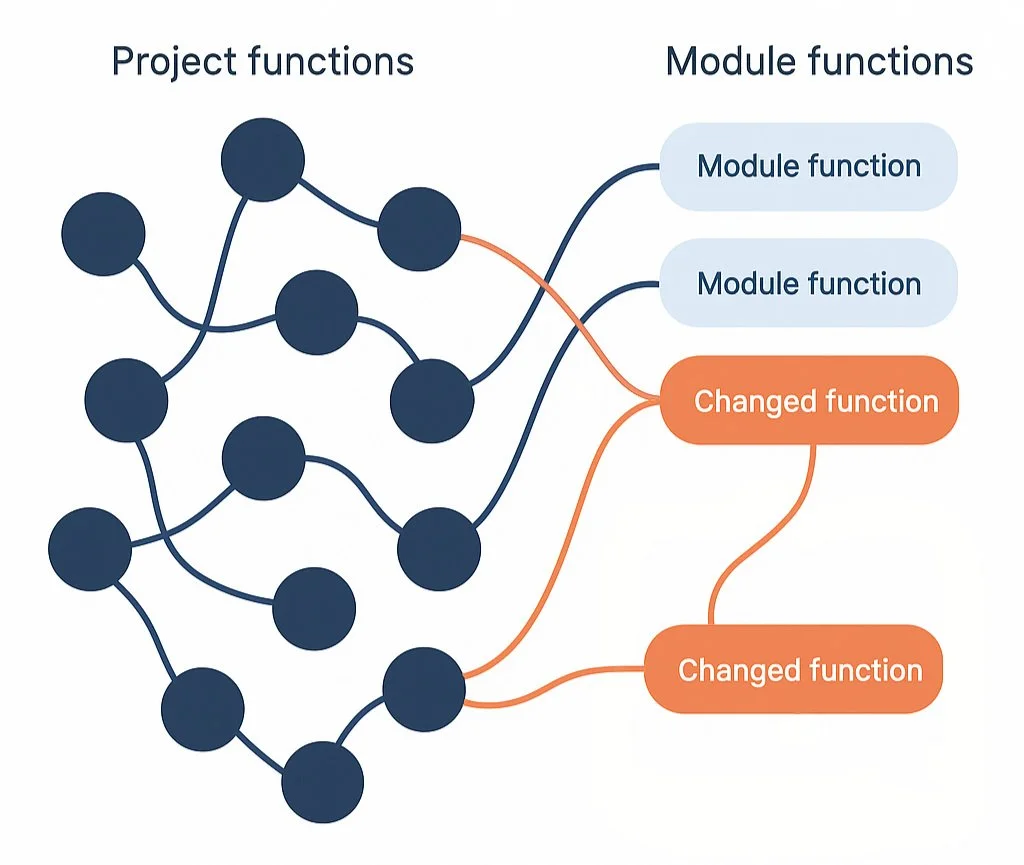
Our tool begins with a detailed change impact analysis. This includes:
Precisely identifying what has changed (including indirect dependencies)
Static code analysis to map how the project interacts with the dependency changes
Identifies security sensitive operations on the network, filesystem, OS, as well as attempts at obfuscation and data or credential exfiltration techniques that could indicate zero-day supply chain compromises.
2. Expand
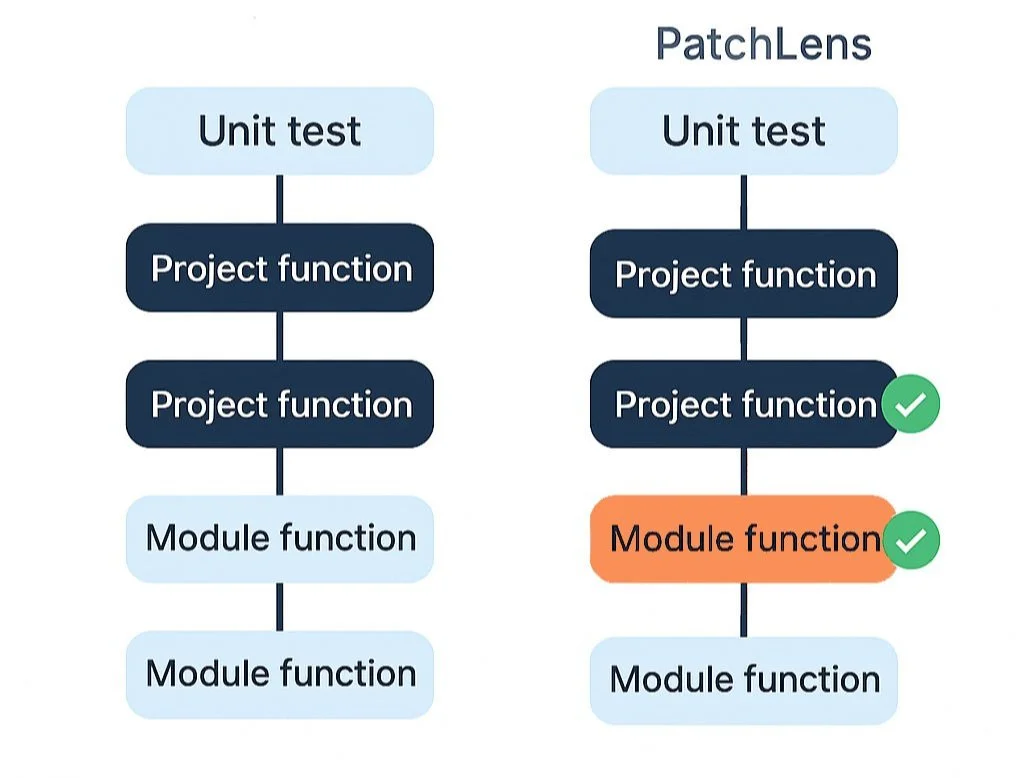
After understanding dependency changes and project interactions, we expand testing coverage to validate stability:
Identifying valuable points to monitor field values across the project. Allowing us to witness behavior changes anywhere in the project, not just at the unit test validations.
AI-powered expansion of test execution to improve change behavior coverage.
The advantage to our field level inspection is that the test expansions don’t need to concern themselves with assertions. Instead we just complete the coverage and use the field analysis to determine if there is a behavior change.
By having such a detailed analysis done prior, we can ensure that our field state checks, and later the validation step targets only areas of the project and module that are relevant for the change. This keeps our tool fast. Our techniques are very detailed, and must be targeted in order to have reasonable execution times.
Once prepared, our tool is aware of the intersection from the dependency change and the project. We must then validate:
Are there obvious test failures to consider, if so we try to detect where the behavior change started.
At points where the project intersects a call path to a changed module function, are there any internal field or behavior changes.
The confidence that the tool was able to validate that behavior change.
Risk is determined by performing a combination of unit testing and the field analysis described in the expand section above.
We determine confidence by:
Validating that the expanded test suite reach the targeted change points.
Introducing synthetic bugs at the logic changes within the dependency to confirm the tests can detect them.
3. Validate
Beyond functional validation, PatchLens specifically elevates security concerns by monitoring how dependencies interact with security-sensitive operations. Even when code accessing sensitive resources isn't new, we flag any behavioral changes—like a networking library suddenly connecting to unexpected servers, or a utility attempting to access credential files. This runtime analysis helps detect zero-day supply chain attacks where malicious actors subtly alter legitimate package behavior to exfiltrate data or compromise systems.